Sikorsky S-92 X Plane 11 Free Download
10 things we know about the undercover 10-37B infinite airplane

The U.Due south. Section of Defense force's uncrewed X-37B spy plane is one of the most intriguing spaceships in the world, flying regular covert missions whose purposes aren't fully known. Only over the years, information about the craft, which is also known as the Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV), has come up to light in dribs and drabs. Here, we take a look at ten things that can be definitively said most the secretive space aeroplane.
Basic facts are available
The reusable 10-37B, which resembles a smaller version of one of NASA'due south now-retired space shuttles, was originally built by NASA in 1999, as previously reported past Live Science's sister site Infinite.com. It is around 29 feet (8.8 meters) long and 9.5 feet (2.9 m) tall, with a wingspan of slightly less than 15 feet (4.6 grand). Information technology weighs 11,000 pounds (iv,990 kilograms) when on the launchpad.
Similar the space shuttle, the X-37B takes off vertically and is propelled by a rocket. Once in orbit, it can maneuver on its own, and it eventually lands on a runway back on Earth, much like a conventional plane. The vehicle has a small payload surface area, roughly the size of a pickup truck bed, enabling information technology to bear gear and satellites. Information technology operates at an altitude of betwixt 150 and 500 miles (240 to 805 kilometers) above World, according to its manufacturer, Boeing.
Different military branches take had it over the years

NASA transferred 2 X-37B vehicles to the Pentagon's Defence force Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in 2004, according to Space.com. After being operated by the U.Southward. Air Force for many years, the robotic spy planes came under the purview of the newly established Space Force in 2020, co-ordinate to Military.com, a news and resource website for armed forces members.
Nobody knows quite what information technology's up to
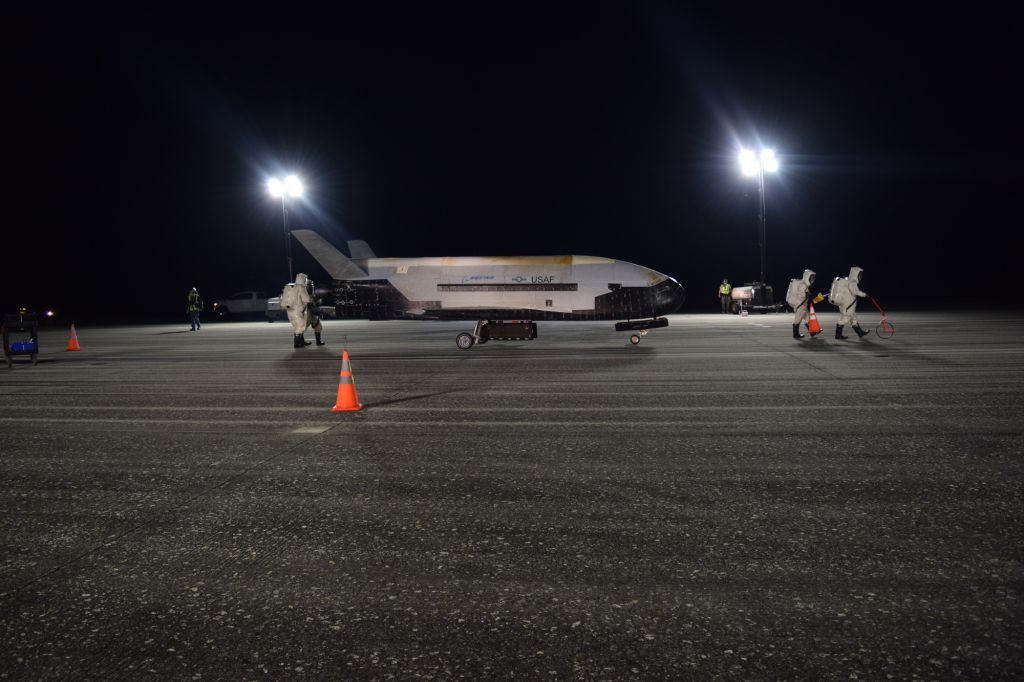

Despite flying six missions to engagement, the X-37B's true purpose remains a mystery. Some possibilities include surveillance of the Earth's surface from on high and deploying spy satellites, though nothing has ever been confirmed.
More out-there theories have been proposed, such as the notion that the 10-37B could be a space-based bomber, a vehicle for spying on the Chinese infinite station, or a means for the U.S. armed services to interfere with other countries' satellites. Experts have splashed cold water on all these ideas, saying they would require large amounts of fuel or would be too easy to trace back to the American war machine, equally previously reported by Live Science.
It can remain in infinite for years
I of the two X-37Bs achieved its first launch in 2010 and spent 224 days in infinite. Its partner vehicle start flew a year subsequently and remained in orbit for more than than double that corporeality of time.
The current record for the spacecraft is 780 days — more than than two full years — in orbit, which occurred during the fifth flight of the X-37B, Live Science previously reported. What it was doing up there for all that fourth dimension remains a mystery.
It can launch on a SpaceX rocket
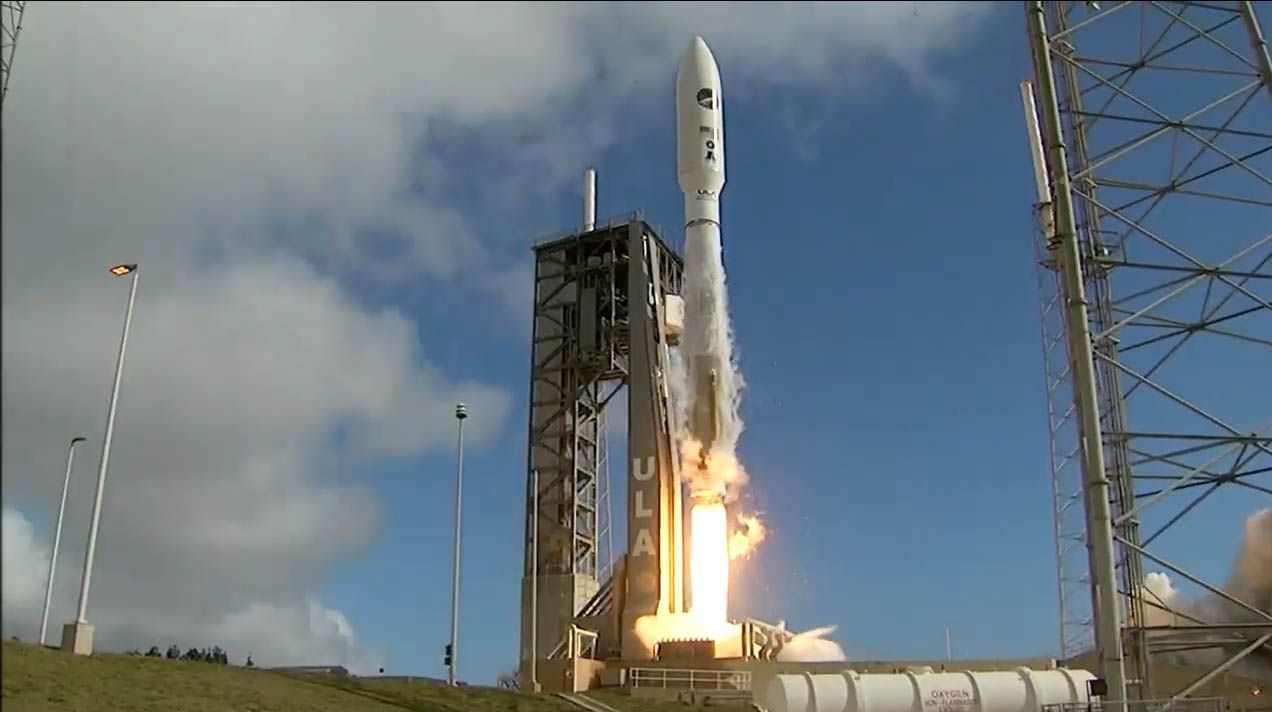

While the X-37B has typically ridden United Launch Brotherhood's Atlas V booster into space, the vehicle is capable of being launched by different rockets. During its fifth mission in 2017, the military changed things up a bit and used a SpaceX Falcon ix rocket to have information technology to orbit, according to Space.com.
Civilians have photographed an X-37B
Though it is a cloak-and-dagger piece of armed services hardware, the 10-37B is non immune to being spotted by civilian skywatchers. The vehicle'southward launch times are publicly announced, which enabled satellite tracker Russell Eberst of Edinburgh, Scotland, to decide where it would be in the sky and see it through a telescope in Oct 2017. Netherlands-based sky sleuth Cees Bassa did the same that yr, Live Science previously reported.
And a Dutch skywatcher and satellite tracker named Ralf Vandebergh was able to photograph the robotic vehicle as it orbited overhead in 2019. "Nosotros can recognize a bit of the nose, payload bay and tail of this mini-shuttle, with even a sign of some smaller detail," he told Live Science at the time.
Information technology can carry experiments
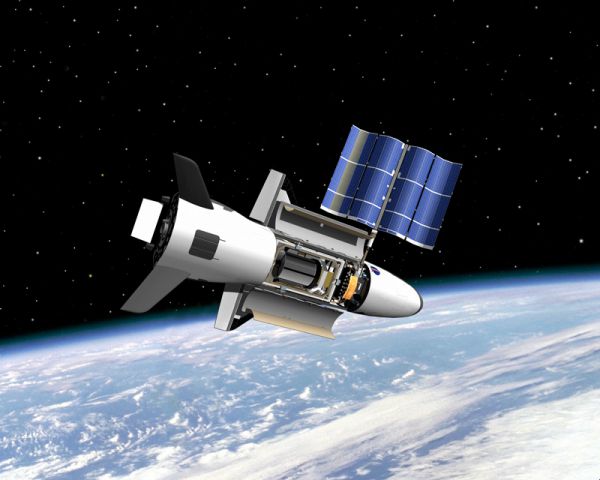

Presently before the most contempo 10-37B launch in 2020, the U.South. armed forces revealed that the spy plane had a new service module attached to its rear that allowed for large numbers of experiments to exist carried to orbit. "The incorporation of a service module on this mission enables u.s.a. to continue to expand the capabilities of the spacecraft and host more experiments than any of the previous missions," Randy Walden, director and program executive officer for the Department of the Air Strength Rapid Capabilities Part, said in a statement.
The mission deployed a small satellite known as FalconSat-8, which independent five experimental payloads, some developed by the U.S. Air Strength and some developed by NASA. While NASA has stated that it was flight an experiment on a previous X-37B flight, this was the commencement time the military had disclosed any specifics well-nigh such cargo.
Information technology has won awards

In 2020, the X-37B was given the Collier Trophy, 1 of the nigh prominent awards in aviation, for pushing "the boundaries of flight and space exploration," according to the U.S. Air Force. "Sophisticated and uncrewed, the X-37B advances reusable spaceplane technologies and operates experiments in space that are returned for farther examination on earth," Secretary of the Air Force Barbara Barrett said in a statement.
Previous Collier Bays winners include Orville Wright, Howard Hughes, the Apollo 11 lunar landing team, the International Space Station, and the B-52.
It is designed to frustrate enemies

During a console at the Aspen Security Forum in 2019, former Air Forcefulness Secretary Heather Wilson revealed that the X-37B may be able to fly low plenty to use Earth'southward temper to alter its orbit, according to Military.com. Wilson said that the vehicle's maneuvers are specifically designed to drive adversaries such as Russia and China "nuts" because they are unable to predict exactly how it will behave.
A crewed version was once in the works
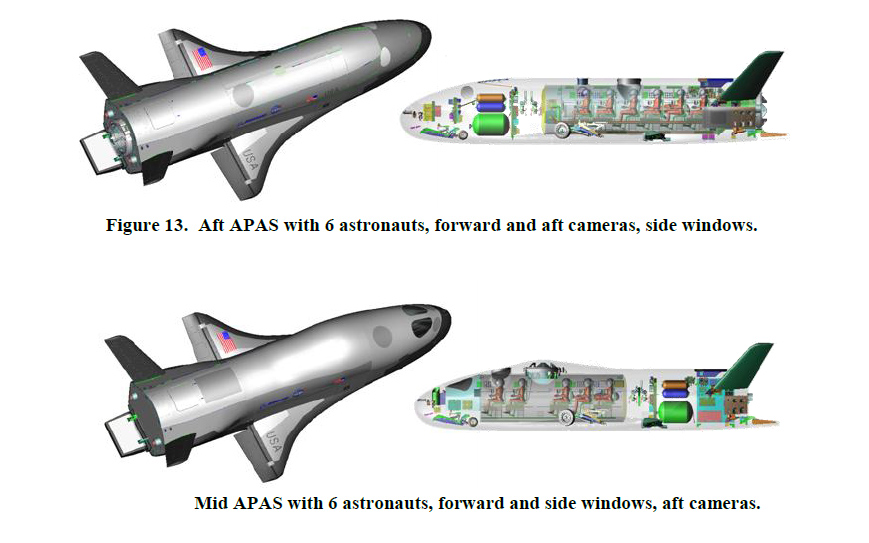
Back in 2011, Boeing studied different vehicle designs that the X-37B could eventually evolve into. A paper by visitor engineer Arthur Granz titled "X-37B Orbital Exam Vehicle and Derivatives" mentioned a version chosen the 10-37C that would be larger and able to bear astronauts, according to Space.com. But since so, picayune information about the X-37C has appeared.
Originally published on Live Scientific discipline.
DOWNLOAD HERE
Posted by: taylorharfugher1979.blogspot.com